
Pricing services feels like a high-stakes gamble for every business owner. Manufacturing cost calculation gives an accurate view of the costs allowing companies to eliminate irrelevant costs and optimize resource utilization to boost profitability. According to the book Manufacturing Cost Estimating, the benefits of calculating the costs of manufacturing range from guiding investment decisions to cost control. Fabrizi also talked about the common challenges manufacturers face when calculating the costs of production. In his experience, the most common challenges are a lack of accurate data and the complexity of costing methods.
Free time tracker
- In that case, the call center’s expenses might be allocated to the manufacturing and sales departments.
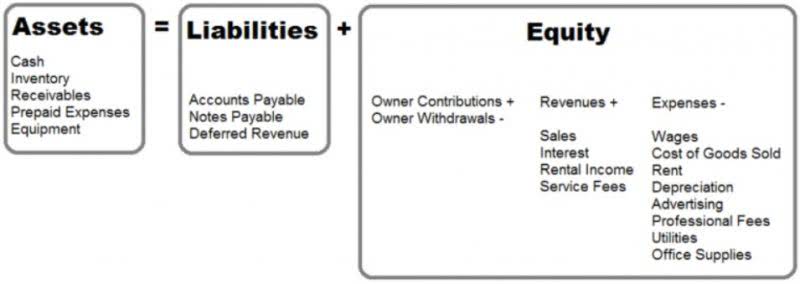
- The total cost of producing goods or services includes all material costs and labor required to produce those goods or services.
- The total cost of manufacturing refers to the cost incurred to produce a product, and it includes the cost of materials, labor, and overhead.
- Accurate cost calculation helps companies identify the processes or materials that are driving up manufacturing costs and determine the right pricing of products — the keys to remaining profitable.
- Manufacturing costs include direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead.
- These include depreciation and amortization for equipment, fixed wages for employees who work on several products, utilities, and property taxes.
In general, overhead refers to all costs of making the product or providing the service except those classified as direct materials or direct labor. Manufacturing overhead costs are manufacturing costs that must be incurred but that cannot or will not be traced directly to specific units produced. In addition to indirect materials and indirect labor, manufacturing overhead includes depreciation and maintenance on machines and factory utility costs. Distinguishing between the two categories is critical because the category determines where a cost will appear in the financial statements. As we indicated earlier, nonmanufacturing costs are also called period costs; that is because they are expensed on the income statement in the time period in which they are incurred.
What Affects The Cost Of Raw Materials? Cost of manufacturing

The demand for skilled workers has increased significantly over the last decade, outpacing the growth of other occupations. As a result, job seekers face a competitive landscape, particularly in their search for entry-level positions. As the world becomes more aware of how important it is to protect the environment and ensure that workers are safe, there are more and more rules to ensure that companies follow these guidelines. Companies have to spend money on complying with these regulations and training their employees on how to comply.
What is the Difference Between the Manufacturing Costs and Production Costs?
If you’re hiring workers to work on your manufacturing line, you can reduce your costs by hiring people who are more efficient at their jobs. You want to make sure they’re good at what they do and that they’ll be able to handle the workload you have for them. The shortage of skilled workers is particularly acute in specific non-manufacturing costs include industries that require specialized skills like manufacturing and engineering. Manufacturing companies often have difficulty finding workers with the right technical skills to fill open positions at all levels of their organizations. The labor market is tight due to the growing demand for skilled workers in manufacturing.

Advertising, market research, sales salaries and commissions, and delivery and storage of finished goods are selling costs. The costs of delivery and storage of finished goods are selling costs because they are incurred after production has been completed. Therefore, the costs of storing materials are part of manufacturing overhead, whereas the costs of storing finished goods are a part of selling costs.

Examples include direct materials, direct labor, and sales commission based on sales. Period costs – are not inventoriable and are charged against revenue immediately. Period costs include non-manufacturing costs, i.e. selling expenses and administrative expenses. Direct material costs are the costs of raw materials or parts that go directly into producing products.

What Is Considered Factory Overhead?
These costs can also be divided into direct and indirect manufacturing costs. Direct manufacturing costs are those that are directly related to the creation of the product itself. Non-manufacturing costs – not incurred in transforming materials to finished goods. These include selling expenses (such as advertising costs, delivery expense, salaries and commission of salesmen) and administrative expenses (such as salaries of executives and legal expenses). Examples of direct materials for each boat include the hull, engine, transmission, carpet, gauges, seats, windshield, and swim platform. Examples of indirect materials (part of manufacturing overhead) include glue, paint, and screws.
What Is Included in Figuring Out the Predetermined Overhead Rate for Manufacturing?
Fuel prices are rising because of the rise in oil prices caused by turmoil in the Middle East and other parts of the world. Companies must pay more to get their products to their customers, affecting their bottom line. The cost of transportation is increasing, putting a strain on manufacturing costs. Table 2.3.1 provides several examples of manufacturing costs at Custom Furniture Company by category. From the table you can see that direct materials are the integral part and a significant portion of finished goods. Examples include advertising costs, salaries and commission of sales personnel, storage costs, shipping and delivery, and customer service.